0002. Add Two Numbers
Description
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
2
3
4
5
Links:
(en)https://leetcode.com/problems/
(中文)https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/
Solutions
此题没什么特别需要注意的地方,主要考验是否熟悉链表,链表的遍历,结点的插入。
Solution1
由于题目给出,需要相加的数字是翻转过后的,因此直接从遍历链表,结点两两相加并考虑进位,直到某一链表遍历完成。
key point: 每次结点值相加时,判断当前结点值是否合法,不合法则从此结点开始遍历到链表尾部进行调整
乍一看,这种实现方式,每次发生进位都进行一次遍历到链表尾部的调整, 好像效率不高。
但是,考虑这样的情形: 当一个数比另一个数大很多时, 小的链表遍历完成算法也完成了
NOTICE: 一个典型的例子: 99999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999 和 1 相加
虽然可以提前终止相加的过程,但是,在代码开始前,需要获取链表的长度来确定哪个数比较大,O(n)
(🤔 不过可以使用快慢指针来提高获取长度的效率,下面的代码没有给出,感兴趣的可以自己实现。)
Complexity Analysis:
- Time complexity : O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Java Code
我解题时的线上提交代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
NOTICE : this apporach will modify the input list.
Complexity Analysis:
Time complexity : O(n)
Space compleixty: O(1)
*/
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
// make the longer list as the number to be added.
int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;
ListNode c;
// calc the len of l1
c = l1;
while (c != null) {
c = c.next;
len1++;
}
// calc the len of l2
c = l2;
while (c != null) {
c = c.next;
len2++;
}
ListNode p, q; // p always point the larger number.
if (len1 > len2) {
p = l1;
q = l2;
} else {
p = l2;
q = l1;
}
while (p != null && q != null) {
p.val += q.val;
if (p.val > 9) {
format(p);
}
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
return len1 > len2 ? l1 : l2;
}
private void format(ListNode list) {
ListNode p = list;
while (p != null) {
if (p.val > 9) {
p.val %= 10;
if (p.next == null) {
p.next = new ListNode(1);
break;
}
p.next.val++;
}
p = p.next;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
submission status
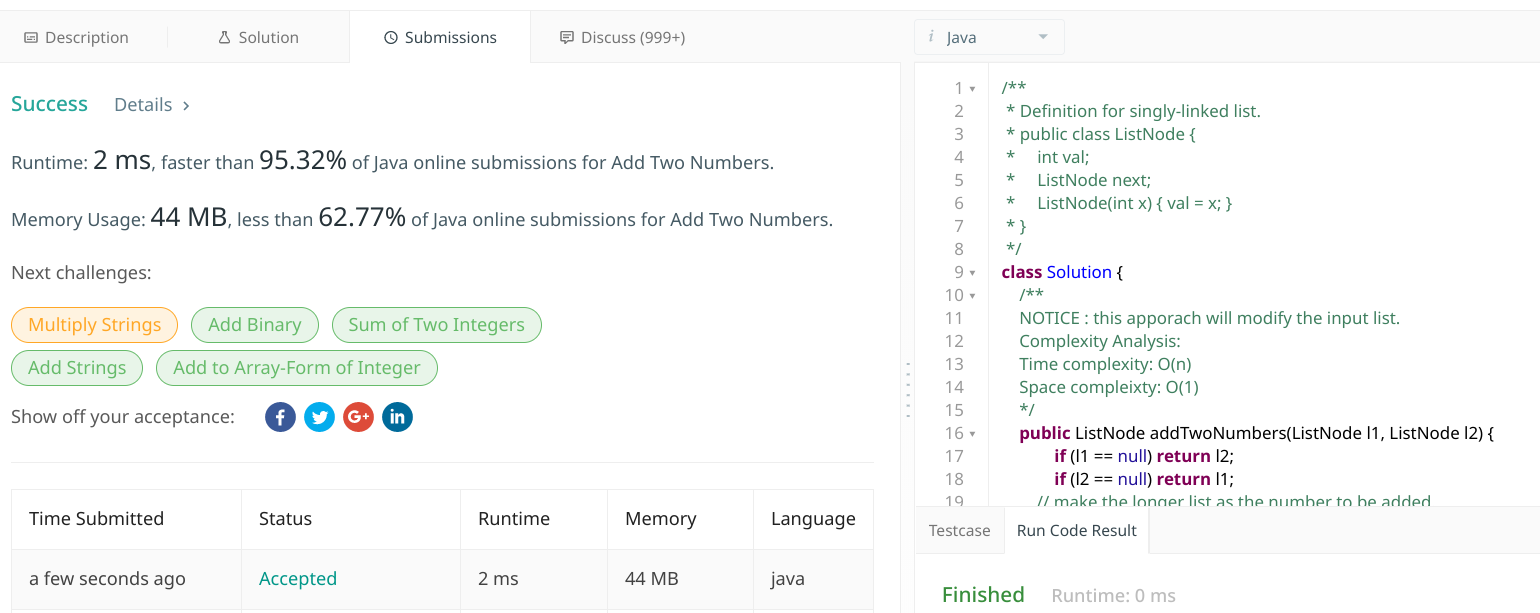
如果你仔细看的话,上面的代码还以进一步优化,😹。
让调整的算法format()可以提前终止,没有需要处理的进位时,避免无意义的遍历操作。
...
private void format(ListNode list) {
ListNode p = list;
boolean flag = true;
while (p != null) {
flag = false;
if (p.val > 9) {
flag = true;
p.val %= 10;
if (p.next == null) {
p.next = new ListNode(1);
break;
}
p.next.val++;
}
if (!flag) break;
p = p.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Solution2
考虑到第一种解法是在一个链表的基础上进行相加的,所以我们可以新建一个来链表来存放两个链表相加的结果(不对输入的链表进行修改)。
🤔不过似乎题目对于是否修改输入的链表也没有进行限定。
Java Code
class Solution {
/**
* since the approach one will modify the input list.
*
* this approach will make create a new list to store the results.
*
* Complexity Analysis:
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(1)
*
* */
public ListNode addTwoNubmer(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
ListNode result = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, cur = result;
int carry = 0;
while (p != null || q != null) {
int x = (p != null) ? p.val : 0;
int y = (q != null) ? q.val : 0;
int sum = carry + x + y;
carry = sum / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
if (p != null) p = p.next;
if (q != null) q = q.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return result.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
这种简易实现方式有一个致命的弱点,我在第一个解法中提到的情况,即当一个数非常的大而另外一个数且相对的小。
此算法遍历的次数是取决于最长的链表的长度的。
Solution 3
此解法综合上面提到的方法,对解法一中的调整算法进行优化,以及解法二中的遍历进行提前终止,然后直接将result的下一个结点指向剩余结点。进行最后一次调整即可。
此算法实现的效率估计和解法一的差不多,但是思路是不一样的。🌚还有,最后还是会修改输入的链表。
Java Code
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode result = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, current = result;
int carry = 0;
while (p != null && q != null) {
int x = p.val;
int y = q.val;
int sum = carry + x + y;
carry = sum / 10;
current.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
current = current.next;
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
current.next = (p == null) ? q : p; // this operation will modify the input list.
if (current.next == null) {
if (carry > 0)
current.next = new ListNode(1);
return result.next; // pointer overflow check.
}
if (carry > 0) {
current.next.val++;
}
format(current.next);
return result.next;
}
private void format(ListNode list) {
ListNode p = list;
boolean flag = true;
while (p != null) {
flag = false;
if (p.val > 9) {
flag = true;
p.val %= 10;
if (p.next == null) {
p.next = new ListNode(1);
break;
}
p.next.val++;
}
if (!flag) break;
p = p.next;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
submission status
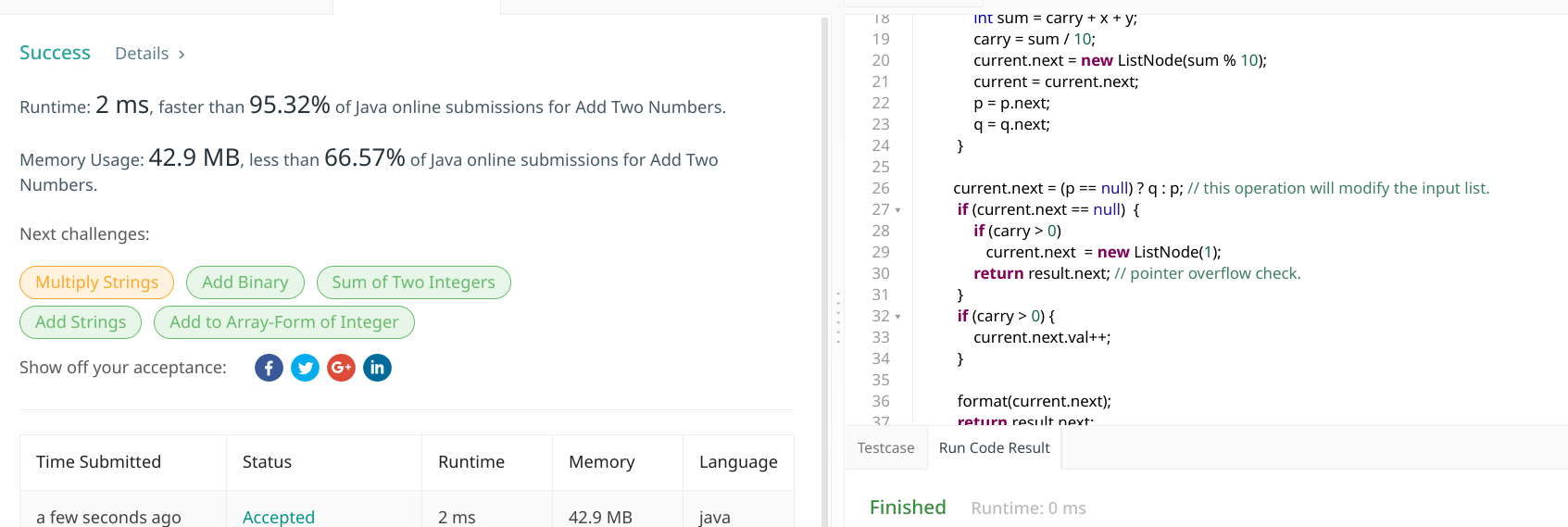
Misc
至于提交代码中,最快的样本,🙄居然是第二种解法,只不过把三元运算符换成if来判断而已。